Guardianship Authority
Presidency of the
Council of Ministers
If you're thinking of starting a business, you’ll need to look at the advantages of each business structure and work out which structure best suits your needs.
Many legal structures are available to establish a business in Lebanon: Foreign investors and Lebanese nationals can equally establish businesses with no restrictions all over the country.
The following table sums up the different types of business structures commonly used:
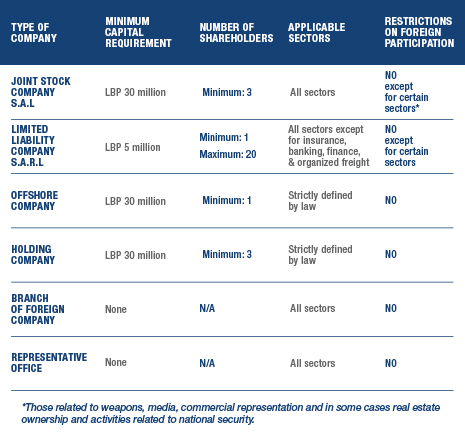
The most common types of business structures for local and foreign investors alike are:
A Lebanese Joint Stock Company (JSC), governed by Decree-Law No 304 of January 24, 1942.
It is constituted amongst shareholders who are only liable to the extent of their contribution and who subscribe to negotiable instruments referred to as ‘shares’.
Lebanese joint stock companies must necessarily have the Lebanese nationality, and must by all means establish their headquarters in Lebanon.
IN BRIEF:
A Limited Liability Company is governed by Decree-Law No 35 of August 5, 1967 and is commonly referred to in Lebanon as S.A.R.L (this is the French equivalent of L.L.C).
The Law No.126 of 29/03/2019, has amended the Lebanese code of commerce, these amendments extended the concept of Limited liability company in accordance with the following principle: The limited liability company is set up by one or more people who only bear the losses up to the amount of their contributions.
IN BRIEF:
A Holding Company is a special type of Joint Stock Company that has a limited object and benefits from special tax treatment and other provisions.
IN BRIEF:
An Offshore Company is a special type of Joint Stock Company (enacted by Decree Law No 46 of June 24, 1983 and its amendments particularly the law no.85 dated 10/10/2018), and to the provisions of this statute. A Lebanese joint stock company (Off Shore) established in accordance with these articles shall be formed by a “Single Partner” who is the sole shareholder, but which operates only in the Lebanese free zone and/or outside the Lebanese territory.
IN BRIEF:
In addition to the above structures an existing local or foreign company can operate in Lebanon through a branch office and do promotion activities through a representative office.
IN BRIEF:
A Lebanese Branch of a foreign company must have the same object as the mother foreign company and can engage in regular trade activities. The parent company must appoint one or more Branch manager to manage and run the Lebanese branch, as well as a lawyer on a yearly retainer basis.
A Representative Office of a foreign company in Lebanon is restricted and limited in its activities to the promotion and marketing of the mother company’s services and products. A representative office may not engage in trade activities of any kind in Lebanon. The parent company must appoint one or more managers to manage and run the Representative Office, as well as a lawyer on a yearly retainer basis.